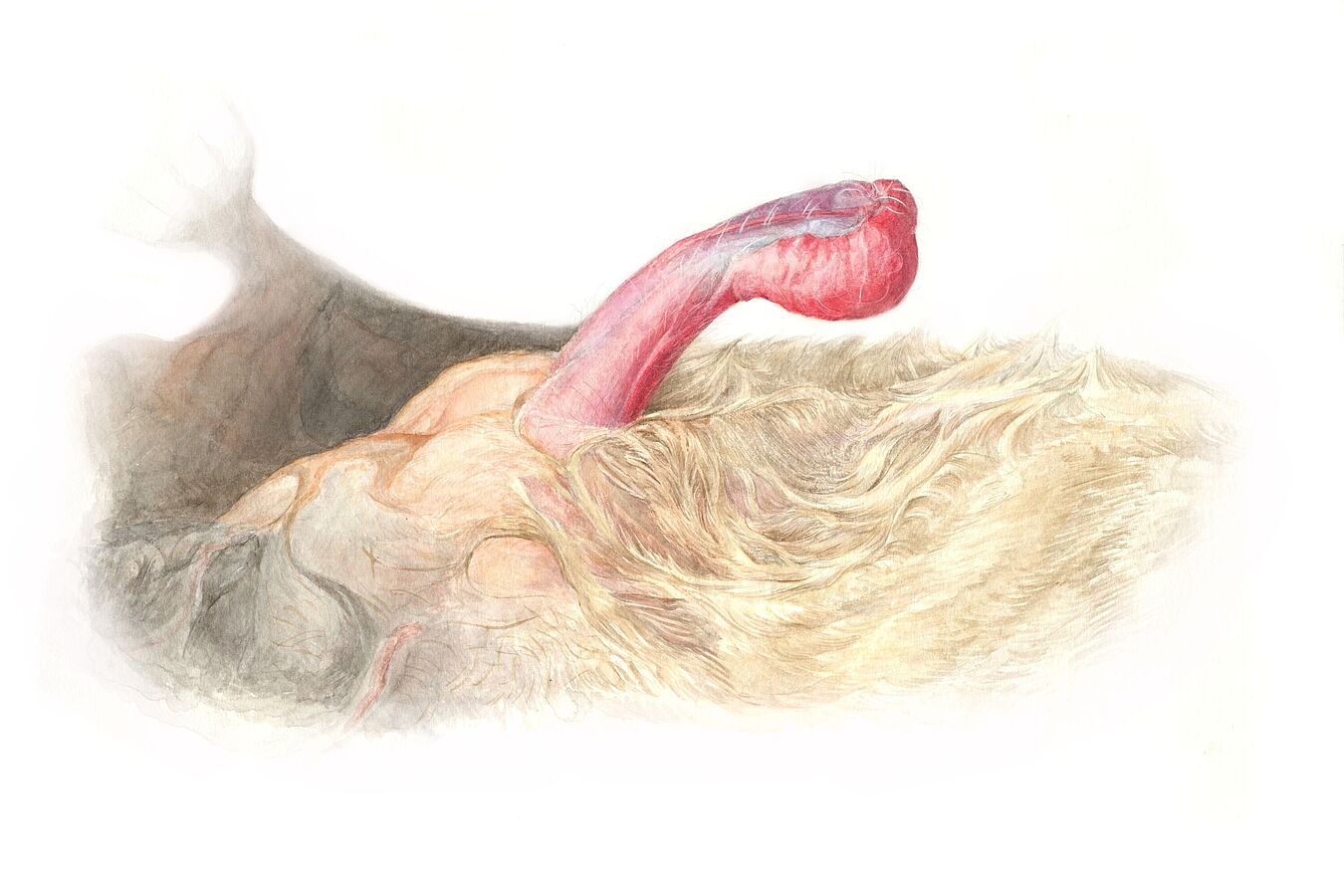
A scientific investigation led by the University of Lausanne and the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW), which was recently published in the journal “Current Biology”, reveals an exception in bats, a group of mammals whose sexual behaviour is still poorly understood. The common serotine bat mates without intromission of the penis into the female genital tract.
The common serotine (Eptesicus serotinus) is a large insectivorous bat found in Europe, the Middle East and Asia. The erect penis in this species is far too large when compared with the size of the vagina of the female. In order to understand how these bats copulate, scientists observed their natural mating behaviour in the attic of a church and during temporary captivity in a bat rehabilitation centre. Live observations of the reproductive behaviour of nearly a hundred pairs showed that the males do not use their penis as an intromittent organ. The male “mounts” the female on the back, as many other mammals do, but the penis is used like an arm to bypass the flight membrane which prevents normal mating. The male applies his penis firmly against the female’s vulva, and the pair may remain in this position for several hours.
This study presents what is a novelty among mammals. The observations and the particular morphology of the penis of common serotine males is the first evidence of reproduction without intromission in a mammal. It is difficult to observe the behaviour of nocturnal animals, and even more so of flying ones, the team of authors write in the journal “Current Biology”. Bats still hold many secrets about their biology. In particular, little is known about their modes of reproduction, which certainly diverges greatly between the 1400 species of bats known to date.