This finding paves the way for increased control of light sources and GHz-to-THz interconversion relevant to quantum technology.
Oscillators with slightly different resonance frequencies tend to lock their frequency to a common value when they start to interact with one another. This phenomenon was originally observed in a system of two pendula sharing the same support by Christiaan Huygens, the inventor of the clock, back in the 17th century [1,2]. Huygens first noticed that it was difficult to make two pendula with the same oscillation frequency—a necessary condition to make precise clocks. If, however, he would hang them on a common support, the clocks would slowly synchronize their motion and, after some time, oscillate at the same frequency.
The synchronization process described above is a general property of oscillating systems known as mode locking or entrainment. It appears in a wide range of oscillators from the very precise time synchronization required for GPS to the synchronization of the human biological clock regulating its daily rhythms. The mechanism behind synchronization is far from trivial. To understand it, we must first consider that the amount of energy stored in a pendulum depends on its frequency and amplitude of motion. In addition, a pendulum can oscillate with frequency within a narrow band, whose width depends on the rate by which the pendulum loses energy (i.e., how quickly the pendulum comes to rest). The frequency locking between the two Huygens’ pendula relies on the exchange of energy via the bar supporting the pendula. This process requires that the narrow band of frequencies of the two pendula overlap, and that the energy transfer rate is much faster than the decay time of their oscillations. If these conditions are fulfilled, energy will be transferred back and forth between the pendula until their vibrations lock to a single frequency. In the locked regime, the net energy exchange between them vanishes.
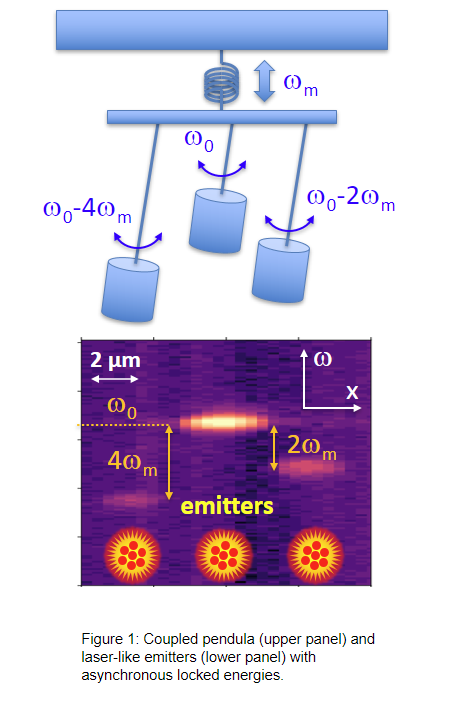
In Huygens’s experiments, the pendula have almost equal frequencies. A new study from the Paul Drude Institute and the Instituto Balseiro set out to demonstrate how one can synchronize the motion of pendula with very different resonance frequencies–i.e., with differences Dw between their resonance frequencies far larger than the frequency band of each pendulum. This scenario occurs if the pendula have different lengths and therefore different resonance frequencies, as is illustrated in the upper part of Figure 1. This process–asynchronous locking of frequencies–is relevant for several applications including the precise frequency locking using phase-lock-loops (PLL) in electronic circuitry as well as the generation of radio waves or light beams with a well-defined frequency difference.
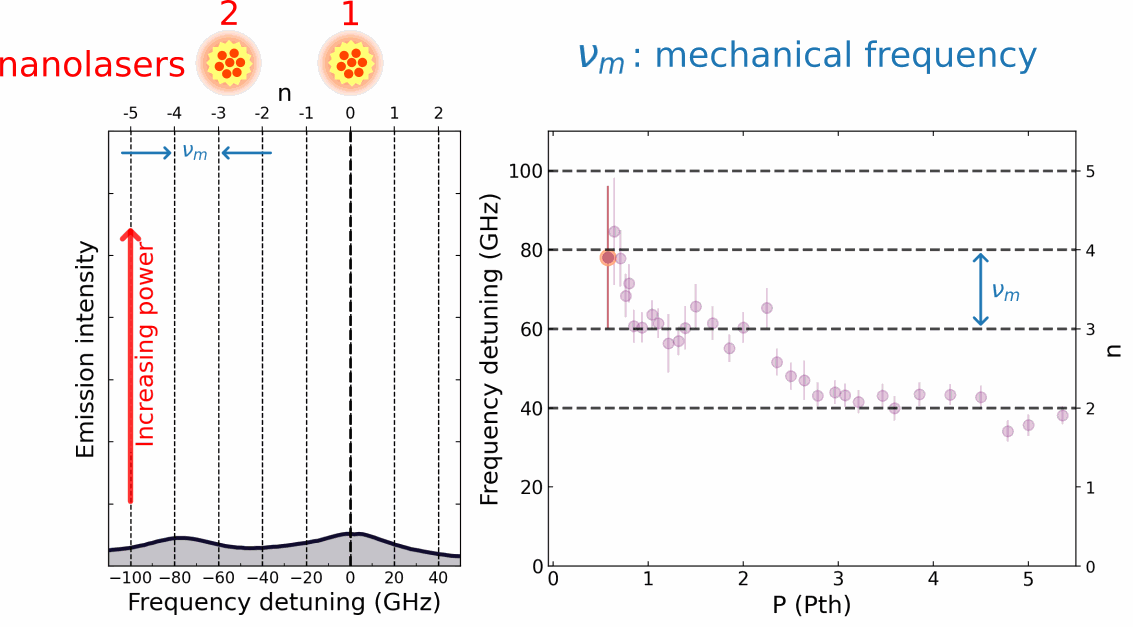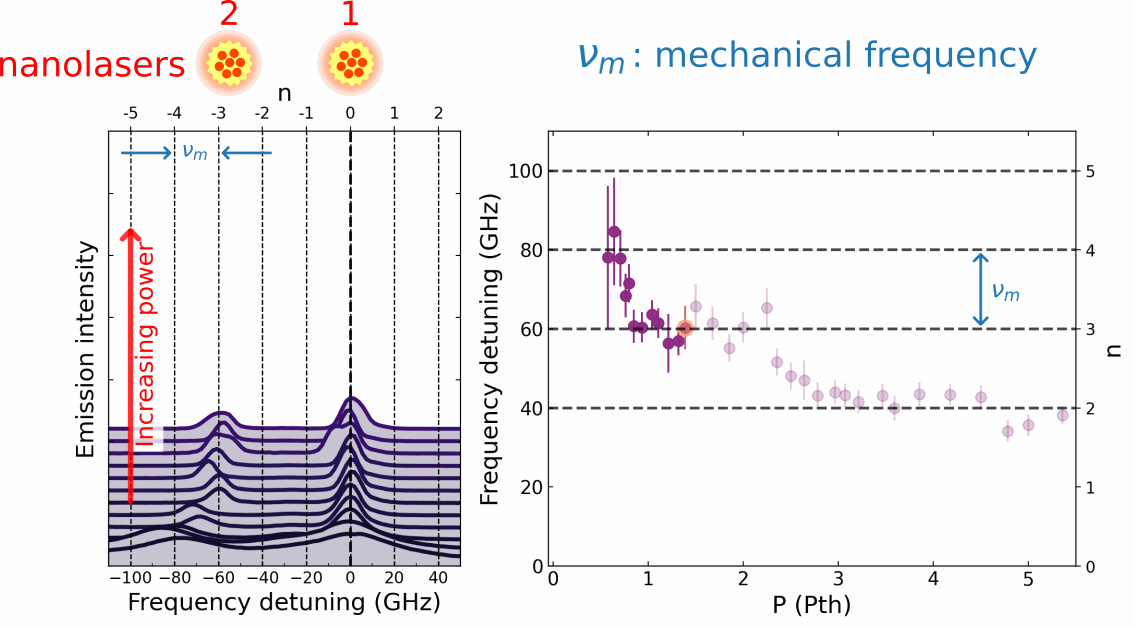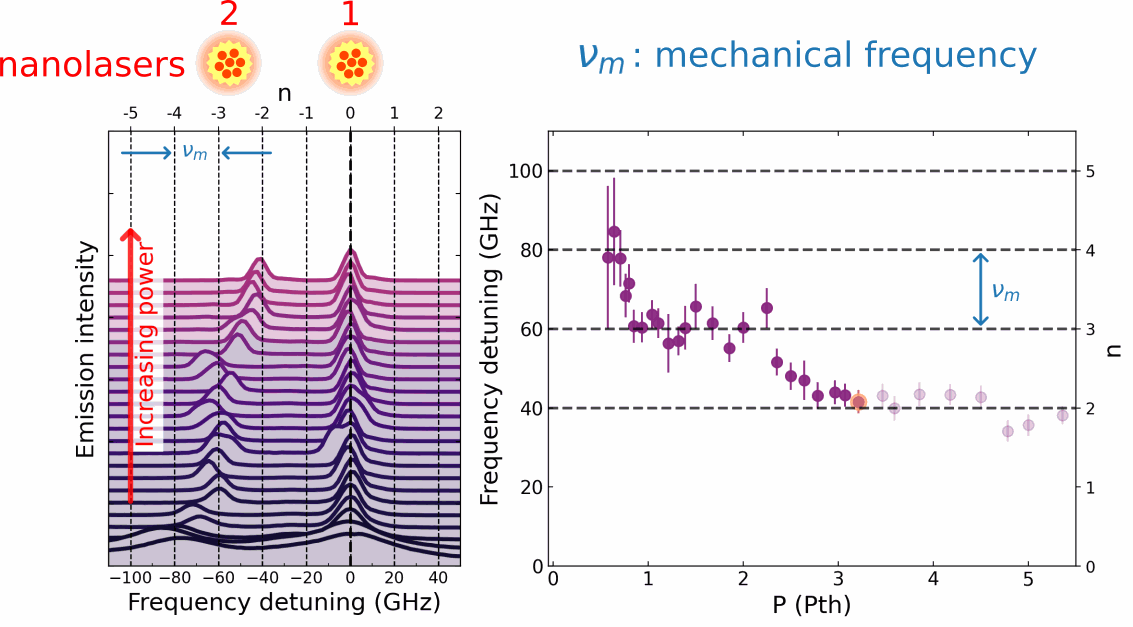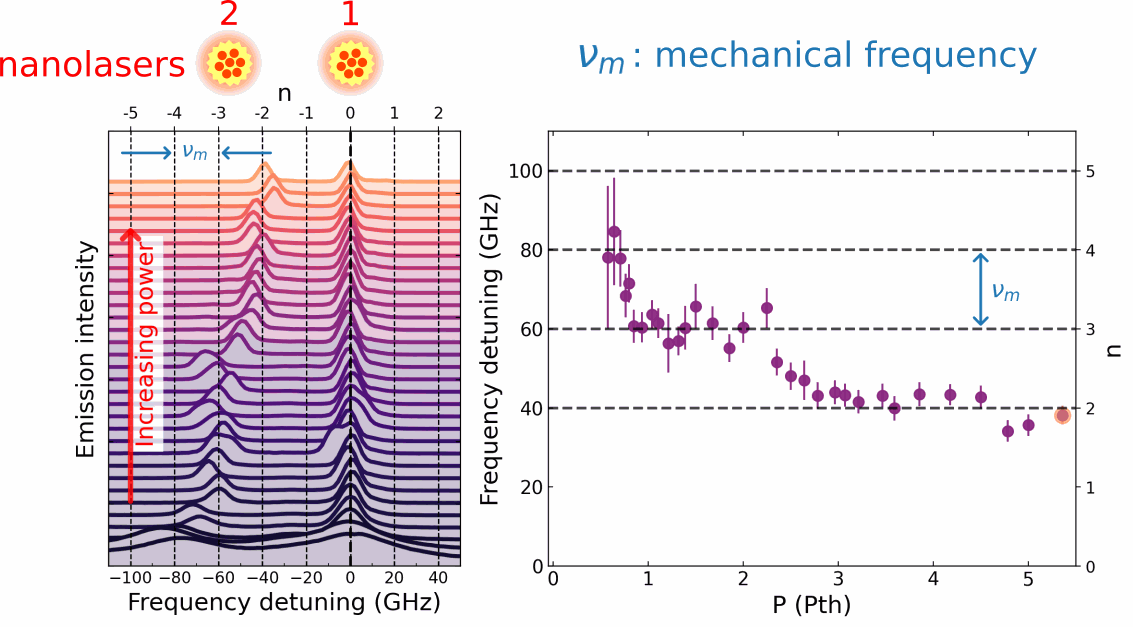
In their publication, Chafatinos et al. [3] demonstrated an integrated array of asynchronously locked laser-like emitters irradiating at frequencies differing by multiples of a well-defined amount/quantity wm. (cf. Figure 1, lower panel). The laser-like light is generated by an array of mm-sized emitters inserted in a hybrid semiconductor opto-mechanical resonator with a mechanical resonance frequency wm of approximately 20 GHz. The emitters are excited by an external continuous wave laser beam. Chafatinos et al. show that the emitters can self-adjust their individual energies under laser excitation until they fulfill the conditions for asynchronous locking. At this point, the relative energy separations between the emitters automatically lock to multiples of wm via the exchange of quanta of mechanical energy. The whole array then starts to self-oscillate at the mechanical frequency wm.
Asynchronous locking in coupled pendula can be achieved by coupling them to a mechanical resonator with frequency wm close to a multiple of Dw (i.e., Dw = n wm , where n is an integer). Such a mechanical resonator is illustrated by the spring-bar system in the upper panel of Figure 1. Energy exchange via the mechanical oscillator provides the frequency offset required for locking. In fact, it can be shown that the requirements for asynchronous locking are the same as the ones for conventional locking when this frequency offset is taken into account. An analogous process occurs for the array of light emitters in the lower panel of the figure. Here, the optomechanical interaction excites vibrations [4] and, simultaneously, induces the energy offset required for asynchronous locking. Interestingly, a quite similar asynchronous locking behavior has been reported recently in a completely different context: the Pitangus sulphuratus, a bird from the Americas, manages to lock the frequency difference between its two vocal cords [5].
The work of Chafatinos et al. demonstrates a new concept for optomechanical materials based on arrays of mm-sized centers strongly interacting with confined GHz vibrations. These results pave the way for ultrafast GHz coherent mechanical control of light sources and interstate transitions relevant for quantum technologies.